When it comes to purchasing new hosting for your website, a world of choices opens up to you, as hosting companies offer a variety of packages, each catering to different website needs. Some offer ready-made packages, while others allow you to customize server resources to your site’s exact needs.
You will face challenges in choosing the appropriate resources that enhance your site’s performance and achieve stability that is compatible with the number of visitors and resource consumption. So, in this guide, we’ll focus on how to determine and measure the right hosting resources for your site, from storage capacity and RAM to CPU and other factors. Our goal is to help you make an informed decision about a hosting plan that perfectly matches your site’s needs, and how you plan to expand resources in the future
How to select the appropriate hosting resources for your site’s requirements
First, the hosting server consists of several main resources that affect the performance and stability of the server based on the size and extent of your site’s consumption. These resources are as follows:
- RAM
- Storage capacity
- Central processing unit (CPU)
- Bandwidth
These resources must be properly selected in proportion to the size and requirements of your site to ensure hosting stability as your site consumes and future expansions, in addition to providing the best user experience. Therefore, we will explain in detail how to measure and determine the appropriate capacity of all essential resources.
1- Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is used to store your website’s web page files temporarily and quickly. The larger the RAM capacity, the better the performance and speed of your site.
If less than necessary RAM is used, this leads to reliance on main storage memory with a slow transfer rate, causing site pages to load slowly. It may also cause problems for customers, such as not loading all the files and code of the web page, or causing problems such as a 500 Internal Server Error .
In general, it is recommended that the RAM capacity be at least 1 GB. For example, if you plan to create a personal website, such as a business gallery, 1 GB of RAM is enough. If you receive a large number of visitors, the RAM should be increased to 2 GB.
If you are aiming to create a WordPress site, it is preferable to use 1 GB of RAM for emerging sites, and increase it to 2 GB if using many plugins and dynamic codes on web pages as the number of site visitors increases as well.
If you aim to create an online store or educational platform, the RAM capacity should not be less than 2 GB, and it is preferable to increase it to 4 GB as the number of visitors increases.
If you aim to create an online store or educational platform , the RAM capacity should not be less than 2 GB, because it includes a large database of customer data, payment methods, etc., and it is preferable to increase it to 4 GB as the number of visitors increases.
In the case of storing and uploading image or video files on a web page, the minimum amount of RAM is 4 GB, because it consumes a large portion of the total memory space.
If you aim to host more than one website on the same server, the RAM space will be doubled according to the previous distribution, and it is preferable that the RAM in this case be no less than 8 GB.
You may need more RAM if the number of visitors to your site increases and you receive a large number of visits at the same time, which requires downloading more files to RAM. In contrast, you can rely on the caching feature to reduce RAM consumption.
2- Storage capacity
Storage capacity depends on several factors, such as the size and type of website, the type of files used, the number of users, whether data and files are saved or uploaded by users on the website, and other factors.
Therefore, in estimating the storage capacity, it is not possible to suggest an average capacity for blogs, online stores, etc., as we calculated the RAM capacity, but it is preferable to calculate it manually according to your site’s requirements.
First, you should know the average web page size on your site. You can use tools such as GTMetrix or Pingdom and then search for “ Page Size ” as shown in the following image:
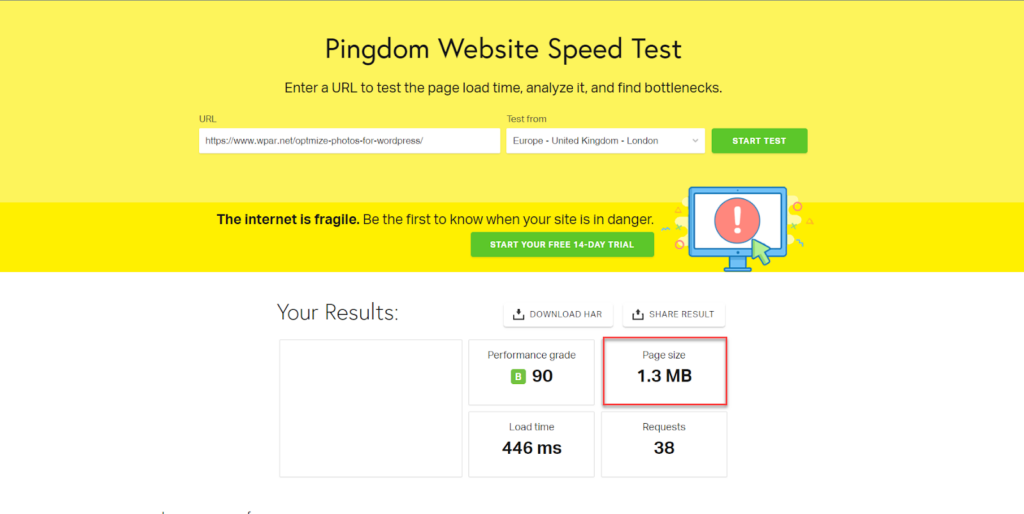
For example, in the previous image, the page size is 1.3 MB, and the size increases as the number of images on the page or video files increases, as well as dynamic codes from live chat, comments, etc.
Therefore, the average page size can be assumed to be 2 MB, and this average can also be relied upon if you do not already own a website to measure the estimated storage capacity of your site.
Next, you must estimate the number of website pages. For example, a personal website may have 10 pages, while an online store may exceed 1,000 pages depending on the number of products, and so on.
The amount of storage required can now be calculated, for example: 100 pages x 2MB = 200MB. To this must be added the amount of annual growth, for example: adding 50 pages per month for a total of 600 pages per year adds 600 x 2 MB = 1.2 GB.
The space of the operating system itself must also be added to the storage capacity, in addition to the rate at which the visitor consumes the operating system and databases. For example, the WordPress system needs 1 GB, in addition to a visitor database consumption and storage rate of 1 MB. If you assume 10,000 visitors per month, the total becomes 1GB + 10,000 x 1MB = 11GB.
The total storage capacity required can be estimated at 200 MB + 1.2 GB + 11 GB = 12.4 GB. It is best to rely on two to three times the required storage space to ensure server stability over the period of use. Therefore, the total appropriate storage space in this case is between 25 – 40 GB.
If you already own a WordPress site, you can rely on the Health Check & Troubleshooting add-on to measure the space consumed by your site’s files and databases. You install the add-on on the site, then choose Tools >> Site Health, and from there choose the Information tab from the top menu, and then Click on the Guides and Sizes tab as shown in the following image:

You review the Total Installation Size tab to see the amount of space consumed by the server, as shown in the following image:

Then you monitor the increase in the total installation size with consumption and normal use of the site for a period of time, for example a month or more, and through that comparison you can estimate the appropriate future storage space for your site.
In addition to the storage capacity, the type of storage unit itself must be reviewed, as hosting companies provide the freedom to choose between an HDD storage unit and an SSD storage unit. It is always preferable to rely on SSD storage capacity as it is more reliable and faster by a large margin.
The fair usage policy must also be taken into account, which refers to the number of files that can be stored in the hosting server. For example, a hosting company may offer a storage capacity of up to 100 GB, but it can only store 400,000 files, so you may need to rely on a higher storage plan. Proportional to the number of files to be stored annually.
3- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The processor is the basis of the hosting server, as it contributes to collecting and processing all parts of the website as quickly as possible to ensure that the site appears in its final appearance to the visitor. The faster and more powerful the processor, the more effective it is in processing site functions, which contributes to improving site speed and providing the best user experience.
The processor can be single-core or multi-core (dual-core, quad-core, octa-core or higher). Each core works separately in the CPU, enabling it to process several jobs at the same time, thus improving visitor response speed.
In case of shared hosting, all site commands are processed using a multi-core processor. But if a large number of commands are processed at the same time, this may overload the central processing unit (CPU), which can cause the site to slow down or crash, which is one of the biggest problems with shared hosting .
In general, there is no fixed rule for determining the hosting CPU resources of your site. However, it is tied to RAM, where the CPU takes directions from RAM. It is irrelevant if the CPU is faster than the RAM, as it waits for commands to be loaded into it and then begins processing them. Therefore, most hosting companies automatically associate CPU with RAM.
It is preferable to rely on a dual-core central processing unit (CPU) for WordPress sites, and increase it to a quad-core one for online stores and educational platforms, where you need to process multiple commands such as purchases, payments, etc.
4- Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the amount of data sent to and from the hosting server per month. When a visitor visits your site, the hosting server sends the requested page contents, such as texts, images, videos, and dynamic elements, to the web browser, and this leads to bandwidth consumption.
The higher the bandwidth, the more your site can receive more visitors per month. But when the bandwidth exceeds the maximum, the site may stop for the visitor.
Bandwidth is calculated in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s), based on the size of your site’s pages, the number of monthly visits, and visitor activity within your site.
First, you must estimate the size of the pages based on tools such as GTMetrix or Pingdom , then search for “ Page Size ” as we did in the storage capacity step, if you already own a site. However, if you do not own a site, you can rely on 2 MB as the average size of the pages.
Next, you should estimate the volume of monthly visits to your site. You can rely on Google Analytics reports or other website analysis tools. If you don’t already have a site, you can estimate your expected monthly traffic volume, for example, 10,000 visits per month. You can assume that a visitor visits an average of three pages on your site.
The total bandwidth required for your site can now be estimated by multiplying the average page size x the number of monthly visits x the average number of pages viewed by a single visitor on your site. For example, 2MB x 10,000 visitors x 3 pages per visitor = 60GB/month.
Finally, you should rely on two to three times the previous number to ensure the stability of the server over the period of use, taking into account the amount of site expansion and expected monthly visits in the number of visitors. Thus, the total bandwidth required in this case is between 120-180 GB/month.
A practical example of determining the required hosting resources
Now that we know how to measure and determine basic hosting resources, let’s put the previous points into a practical context through some examples, from startup WordPress sites to online stores.
Choosing suitable hosting for a startup WordPress site
The first practical application, hosting a startup WordPress site with an expected daily traffic rate of 250 visitors, initially requires at least 1GB of RAM. Regarding the CPU, it is preferable to rely on a single to dual-core processor.
As for the required storage capacity, an average of 200 pages are expected to be published per year, and an average page size of 2 MB is assumed. Added to this is 1 GB of WordPress system space, in addition to visitor and database storage consumption at a rate of 1 MB per visitor. Therefore, the total storage capacity required is (200 pages x 2MB) + 1GB + (7,500 visitors per month x 1MB) = 8.9GB per month. The amount of monthly expansions is taken into account by taking two to three times the storage space, with an average of 20 GB.
Finally, for the required bandwidth, an average of 2-3 pages per visitor is charged on your site. The total bandwidth required is 2MB x 7,500 visitors x 3 pages per visitor = 45GB per month. The amount of monthly expansions is also taken into account with a two- to three-fold increase in bandwidth capacity with an average of 100 GB.
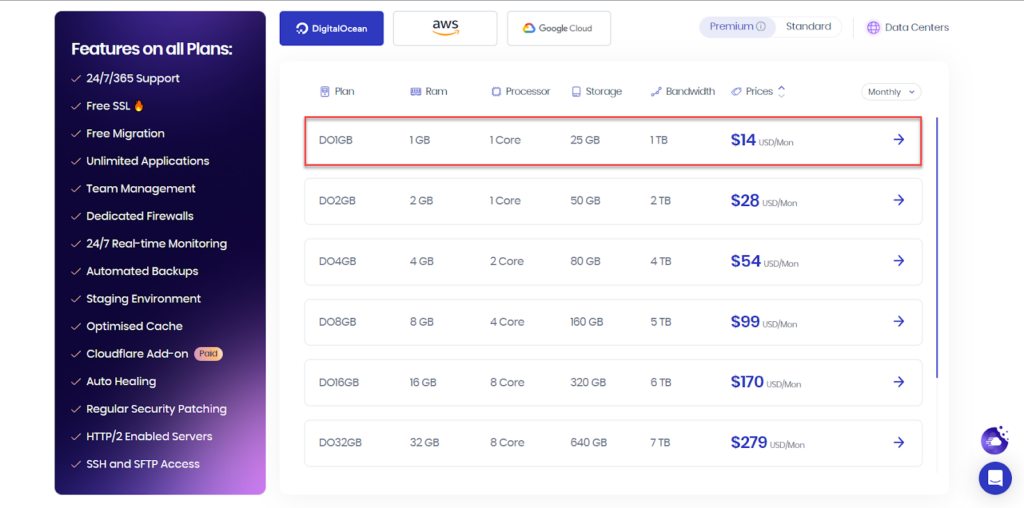
So if you rely on Cloudway hosting , the D01GB plan will be quite suitable, as shown in the following image:
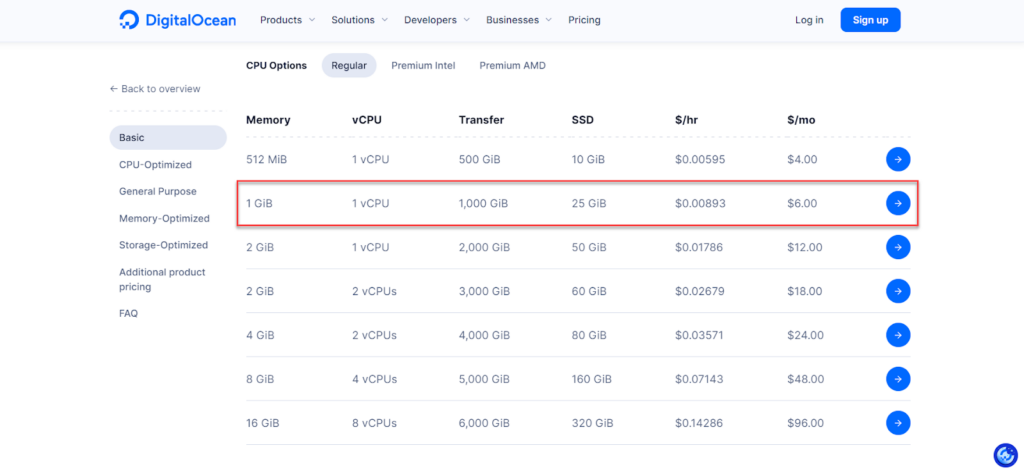
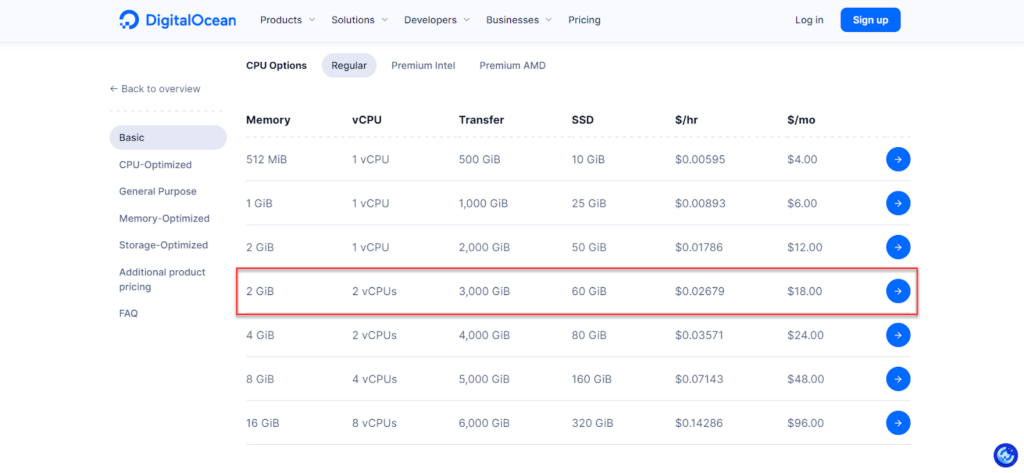
Also, if you rely on DigitalOcean hosting , the second plan will also be suitable for you, as shown in the following image:
Choosing suitable hosting for an online store
The second practical application is hosting an average online store with an expected visitor rate of 1,000 visitors per day. First, the site needs a random access memory (RAM) of at least 2 GB, and it is preferable to increase it to 4 GB. As for the central processing unit (CPU), it is preferable to rely on a dual processing unit. .
As for storage capacity, it is assumed that an average of 1,000 pages or products are published annually, the average page size is 2 MB, the average visitor consumption of databases is 1 MB, and the WooCommerce system space is 1 GB, so the total storage capacity required is (1,000 pages x 2 MB) + 1 GB. + (30,000 visitors per month x 1MB) = 33GB per month. And up to 60 to 90 GB with future expansions.
As for bandwidth capacity, an average of 3 pages that a visitor browses on your site is imposed, so the total is 2 MB x 30,000 visitors x 3 pages per visitor = 180 GB/month. And up to 360 to 540 GB with future expansions.
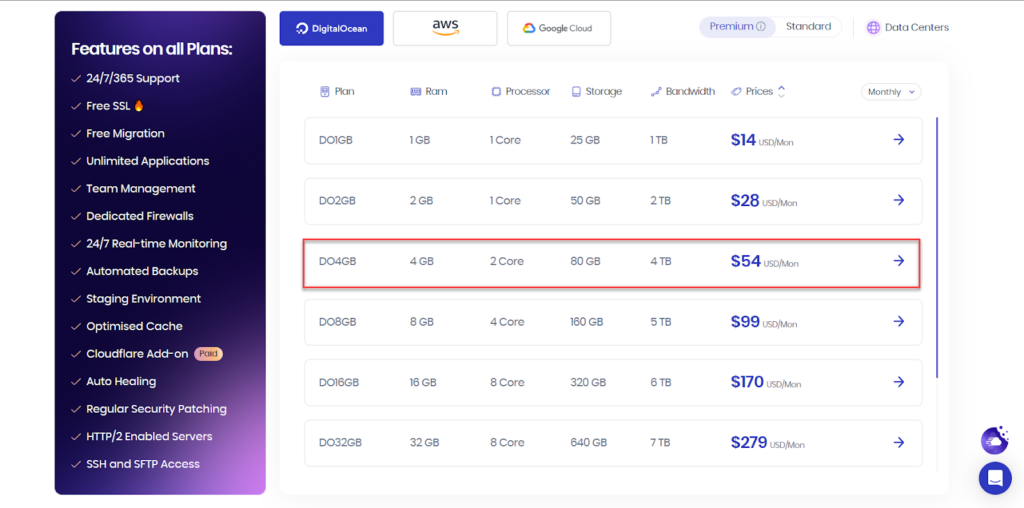
So if you rely on Cloudway hosting, the D04GB plan will be suitable, as shown in the following image:
If you rely on DigitalOcean hosting, the fourth plan will also be suitable for you, as shown in the following image:
After purchasing a hosting plan, it is always a good idea to monitor server resource consumption from the hosting company’s control panel. Server resource consumption must not exceed a maximum of 80%. When this stage is reached, it is an indication that server resources need to be expanded to meet your growing site requirements. Therefore, it is also preferable to rely on hosting companies that offer flexibility in modifying server resources, and the best of these companies are cloud hosting companies .
































Leave a Reply